Diamonds
Shape
Diamonds are cut into a variety of shapes including: Round Brilliant, Marquise, Pear, Emerald, Princess, Oval, Radiant, Heart, and Trillion.
Cut
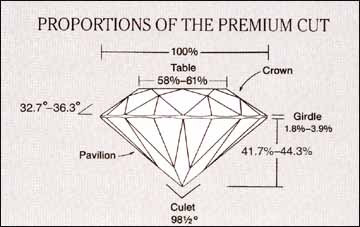
Refers to the brilliance of the cut. Gem cutters have developed the Ideal-cut Round Brilliant which is cut to mathematically ideal proportions for maximum light reflection. In an ideal-cut diamond, all of the light entering the stone is reflected through the top. In inferior cuts that are too deep, light passes through the bottom of the stone and the center of the stone appears dark. In a diamond cut too shallow, light passes through the bottom of the stone and the stone might appear watery or dark or may look as if there is a hole in the center.
Color
Most diamonds have slight tint of yellow or brown. The less color, the rarer and more valuable the stone. Diamond color is graded on a scale from D to Z.
D E F Colorless
G H I J Near Colorless
K L M Faint Yellow
N O P Q R Very Light Yellow
S T U - Z Light Yellow
Clarity
Nearly all diamonds have natural inclusions or flaws in the stone. Flawless diamonds are extremely rare. The size, nature, location and number of inclusions determines the clarity grade of the stone. The clarity grade is based on the following scale:
- FL-IF Flawless / Internally Flawless
- VVS1-VVS2 Minute inclusions extremely difficult to see under 10X magnification to a skilled Gemologist.
- VS1-VS2 Minor inclusions difficult to find under 10X magnification to a skilled Gemologist.
- SI1 Noticeable, easy to find under 10X magnification.
- SI2 Noticeable, very easy to find under 10X magnification. Inclusions may be visible to the naked eye.
- I1 Obvious under 10X magnification. Slightly visible to the naked eye. Brilliance or durability may not be affected.
- I2 Obvious to the naked eye with brilliance or durability seriously effected.
- I3 Obvious to the naked eye with brilliance and durability seriously effected.
Carat Weight
Not to be confused with karat which is the measurement of the purity of gold. Carat is the weight measurement used for diamonds and all precious stones. Fractions of a carat are referred to as points. For example .34 carat may also be referred to as 34 points.
Fancy Colored Diamonds
Diamonds are found in all colors. While the majority have a slight tint of yellow or brown, diamonds are also found with strong colors from Red to Black. Diamonds with these strong colors are graded to have fancy color. Most fancy colors are rarer than white. The most common fancy colors are dark brown and strong yellow. Fancy Colored Diamond’s color is graded based on three criteria: Hue, the basic body color which can be a mixture of colors; Tone, the lightness or darkness of the color; and Saturation, the richness of the color.
Some particular colored diamonds represent the rarest and most precious of all gemstones. One famous example of a colored diamond is the Hope Diamond, a 45.52 carat Fancy Vivid Blue diamond, the largest blue diamond in the world.
Colored diamonds are available in a variety of price ranges. Please contact us for more information on pricing and availability.